THE SCIENCE BEHIND OUR PRODUCT
ALCOHOL ABSORPTION
- Approximately 80%-90% of consumed alcohol [CH3CH2OH] is absorbed through the small and large intestines.
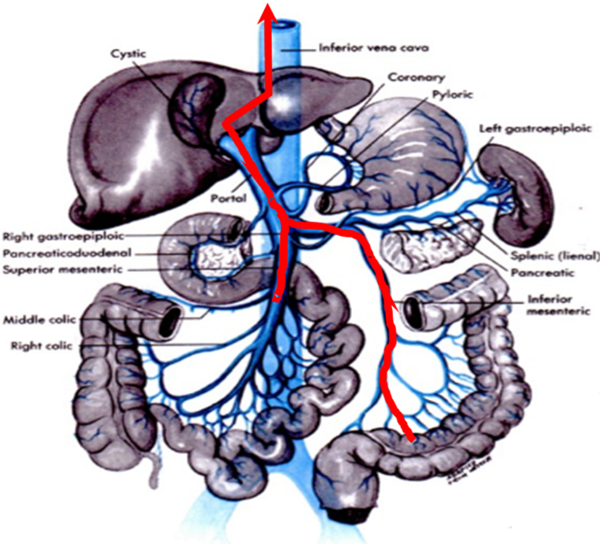
- Once in the bloodstream, alcohol travels through the portal vein into the liver, where it is quickly metabolized (broken down) and oxidized (eliminated) from the body via the Krebs’s or citric acid cycle.
THE LIVER
- The liver is the body’s primary organ eliminating 90% – 98% of all ingested alcohol.
- Daily, the liver eliminates an average of 7 grams of alcohol from our dietary food intake.
- An enzymic metabolic pathway in the liver chemically breaks down alcohol efficiently and neutralizes alcohol’s highly toxic poisonous by-product, acetaldehyde, quickly.
- However, the liver’s alcohol metabolism rate is linear or a fixed rate and limited to approximately 0.5 ounces per hour, (or one drink per hour). A standard drink contains about 0.6 fluid ounces of pure alcohol.
- The liver’s fixed metabolic rate does not accelerate or increase its alcohol removal capacity, regardless of how much alcohol arrives.
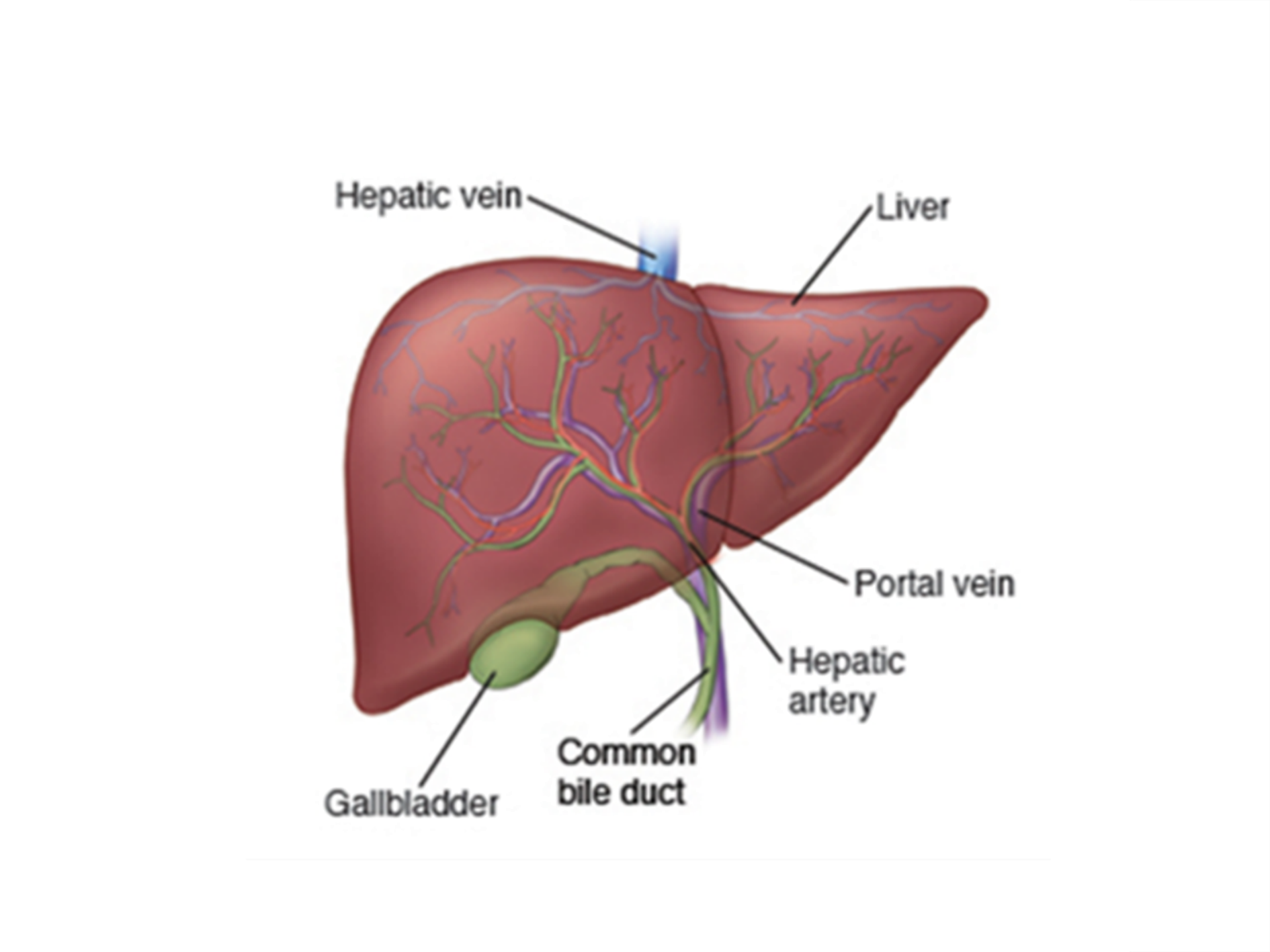
Alcohol's metabolism and Elimination process
The liver, uses two hepatic enzymes to break down and safely eliminate ethanol.
- Alcohol Dehydrogenase (ADH) and
- Aldehyde Dehydrogenase (ALDH)
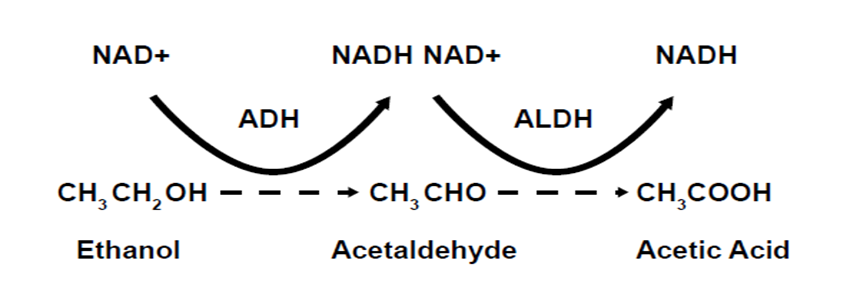
- The ADH enzymes first reduces ethanol, into poisonous Acetaldehyde
- Next, the ALDH enzymes reduces Acetaldehyde into Acetic Acid or Acetate
- The liver then sends the Acetate into the muscles for reduction into harmless
CO2 and H20 for elimination.
- The liver then sends the Acetate into the muscles for reduction into harmless
The ADH enzymes first reduces ethanol, into highly toxic Acetaldehyde.
The ALDH enzymes reduces Acetaldehyde into Acetic Acid or Acetate
Then liver then sends the Acetate into the muscles for reduction into harmless CO2 and H2O for elimination.
An significant point to understand is the liver’s metabolism rate is linear or fixed at approximately 0.5 ounces, (1 standard drink) per hour.
A standard drink contains about 0.6 fluid ounces of pure alcohol.
The blood stream circulates alcohol throughout the body every 90 seconds which is why alcohol’s effects can be felt within 15-45 minutes after the first drink.
when is alcohol a health issue?
- Consuming multiple drinks overwhelms the liver’s ability to eliminate alcohol quickly. Instead, the raw alcohol travels to the heart and is pumped throughout your body.
- The heart continues to circulate raw alcohol throughout the entire body every 90 seconds.
- As a result, alcohol rapidly builds up in the blood stream raising your Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC) levels.
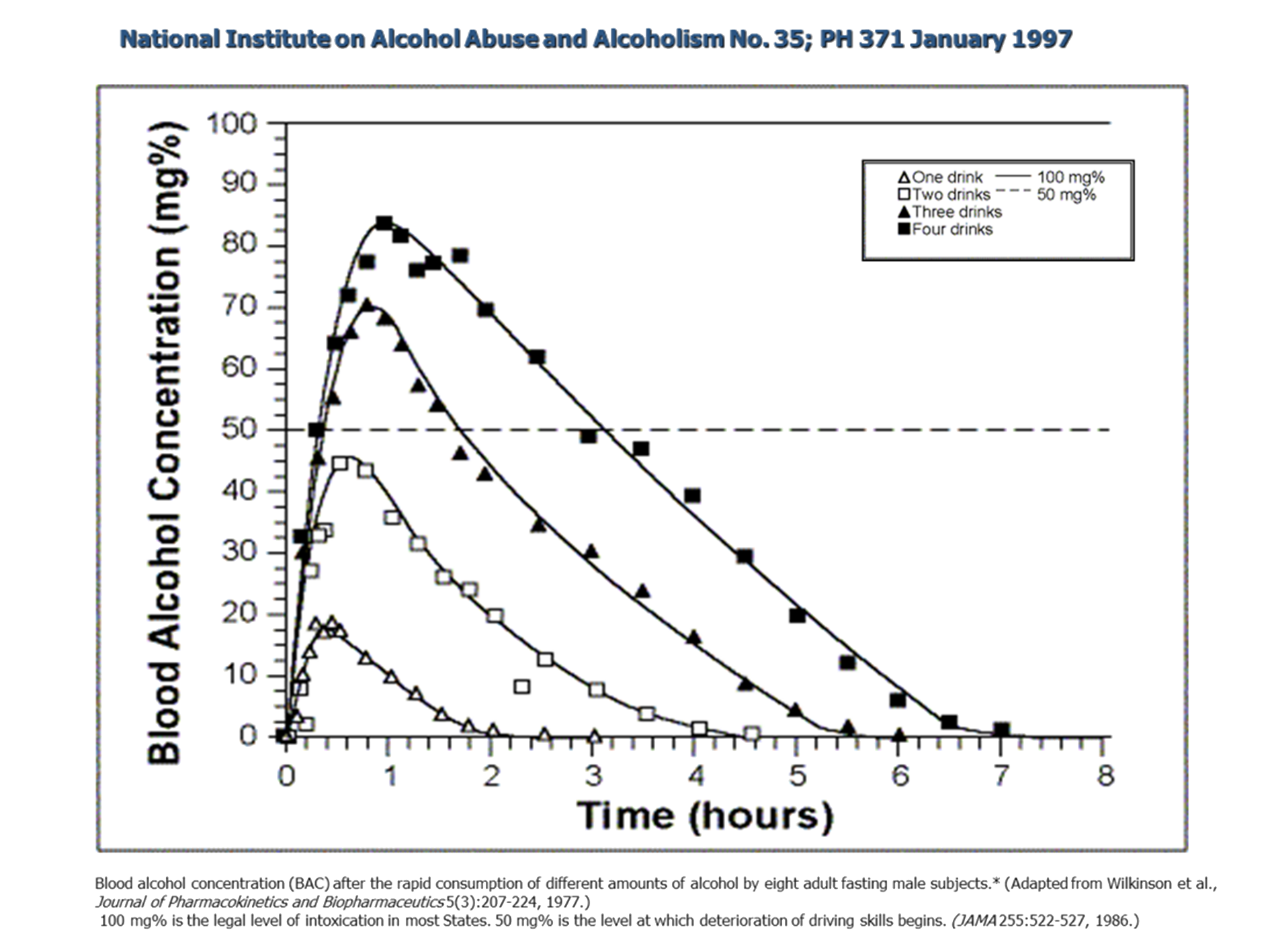
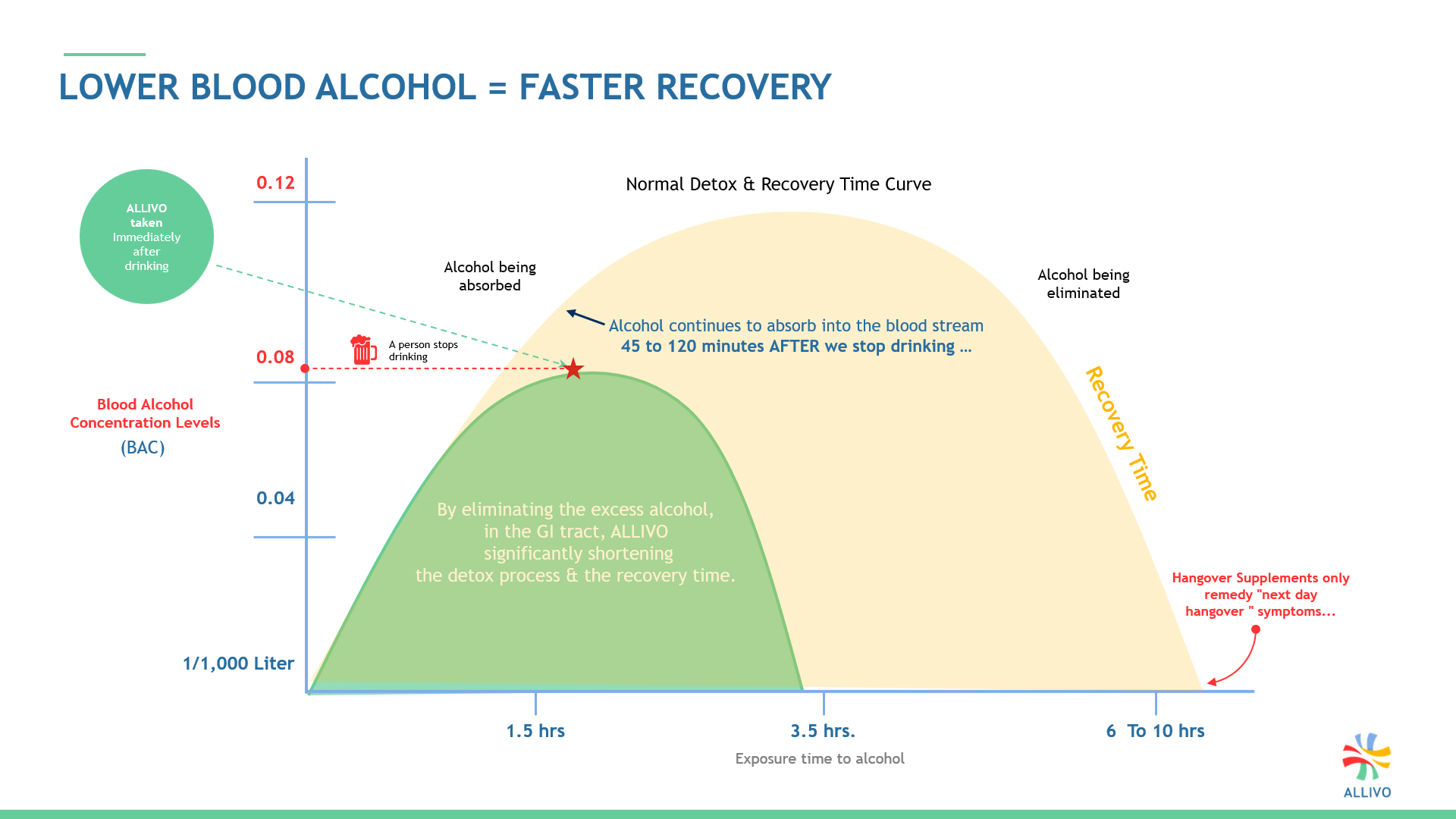
- Just 4 drinks can take the liver 6 to 7+ hours to breakdown and clear the alcohol from your bloodstream. {see graph}
- An individual’s actual detoxication time varies based on their weight, gender, age, body mass, stomach food, content, alcohol consumed, etc.

In other words, the more you drink…. The longer alcohol stays in your bloodstream….
The longer it stays in your bloodstream…. The more damage occurs to your cells and organs!
Over time, this is when alcohol becomes a health issue.
In other words, the more you drink…. The longer alcohol stays in your bloodstream.. The longer it stays in your bloodstream…. The more damage occurs to your cells and organs! Over time, this is when alcohol becomes a health issue.
alcohol's cellular damage
- Alcohol readily dissolves in water. Our body is 55%-60% water.
- As a result alcohol can easily penetrates the cellular membrane and your body’s organs.
- These non-hepatic (non-liver) cells are not equipped to breakdown and efficiently eliminate alcohol quickly the way the liver cells can.
- When this happens, a toxic environment develops inside the cell called Oxidative Stress.
- Free Radicals, highly reactive, unstable oxygen molecules, form disrupting the cell’s homeostasis and destroying cell DNA (see below).
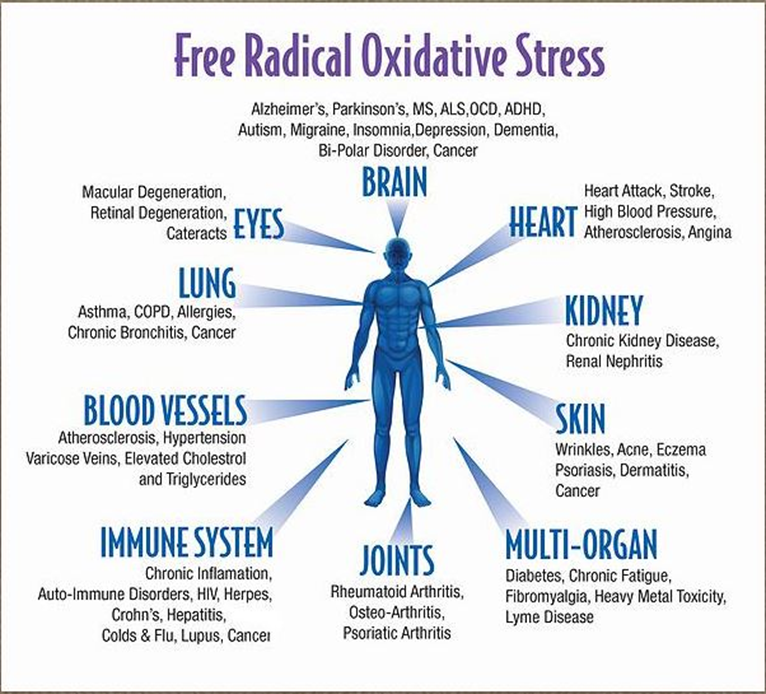
Over time, these damaged cells become susceptible and a major contributors to over 200 known diseases and disorders, like:
- cancer,
- cirrhosis,
- cardiovascular,
- inflammation,
- stroke,
- diabetes, etc.
Research has proven the only effective way to avoid alcohol’s long-term health risks is reduce your body’s exposure to alcohol’s poisonous by-product, acetaldehyde.
Current products, focus primarily on providing relief for the “hangover” symptoms, like headaches, nausea, dehydration, etc., instead of helping the liver minimize the root cause, cellular destruction.
The scientific community offer few answers other than suggesting … “don’t drink”, or “drink in moderation”.
So you say….”If the body has an alcohol metabolism system to eliminate the alcohol we consume what is the problem?”….
The problem is not the alcohol. Thew problem is how much alcohol we drink!
The liver can ONLY remove one drink each hour. Beyond one drink per hour, alcohol turns toxic to the body’s organ and tissues.
There are no current products that address how to increase the liver’s capacity to speedup the elimination of the multiple drinks consumed.
That is until now!!
THE ALLIVO SOLUTION:
Antidote:
“a substance that cancels or reduces another substance’s poisonous effects.”
Alcohol has both short-and long-term poisonous effects on the body.
Allivo works like an antidote… reducing how much of the alcohol you just drank is absorbed into the bloodstream.
Our all-natural formula replicates the body’s own enzymic pathway using probiotics and co-enzyme catalysts to create a metabolic pathway inside the stomach making the unabsorbed alcohol bio-unavailable.
With less alcohol arriving, the liver can clear the circulating blood alcohol faster, dramatically shortening the intoxication, reducing the body’s exposure time to alcohol’s toxic byproducts, (i.e. acetaldehyde, free radicals).
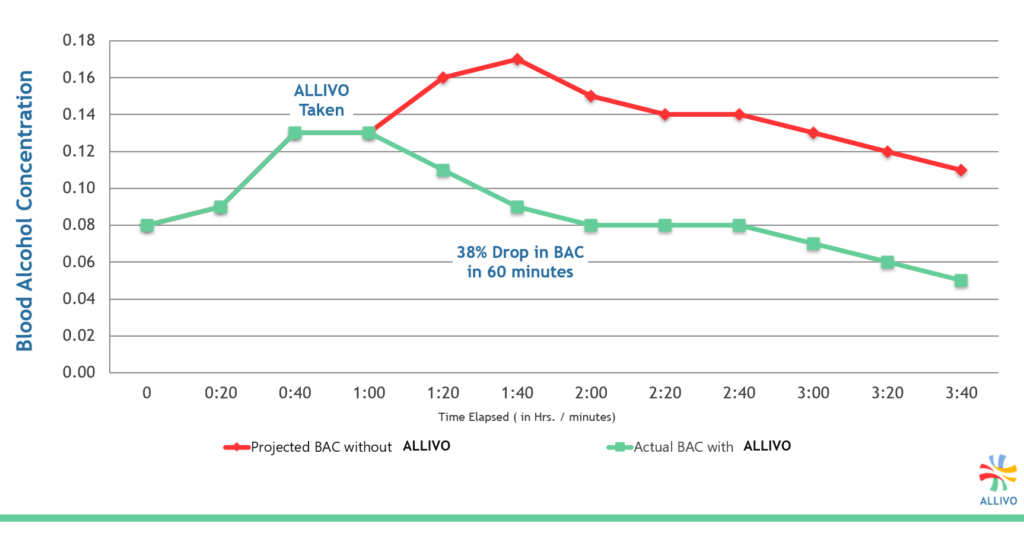
Trials conducted with volunteers show the sooner someone takes the formula, either during or immediately after drinking, the greater ALLIVO’s metabolism impact aids the liver.
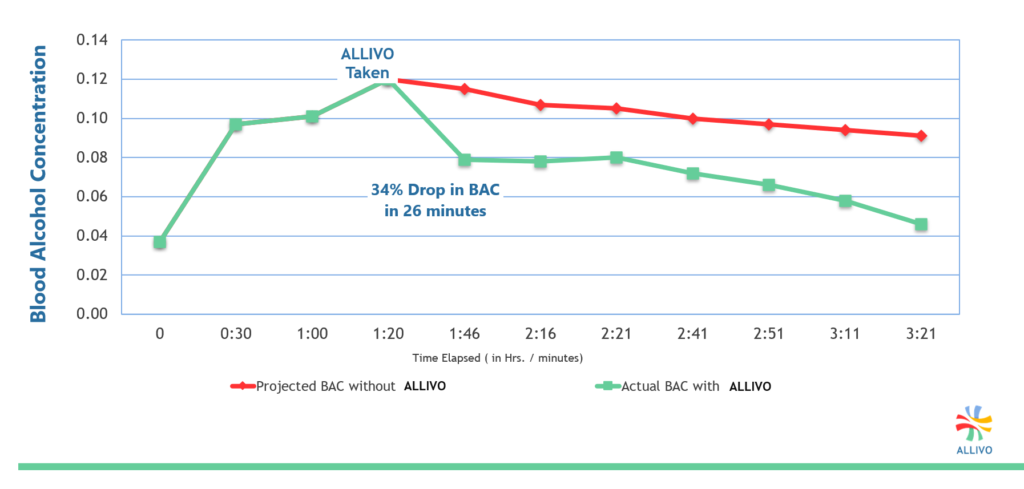
Pharmacokinetics graphs are used to illustrate the reduction over time of a subject’s blood alcohol concentration (BAC) levels.
A pharmacokinetic or (ADME) curve measures the time it takes a substance to be absorbed into the body, distributed throughout the body, metabolized into its by-products, then finally eliminated from the body.
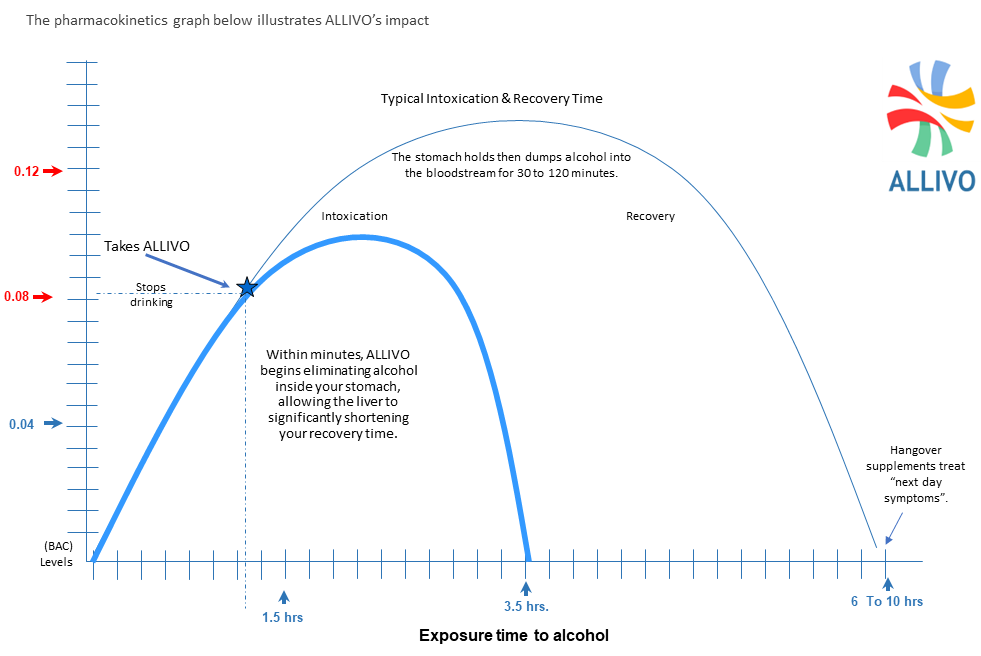
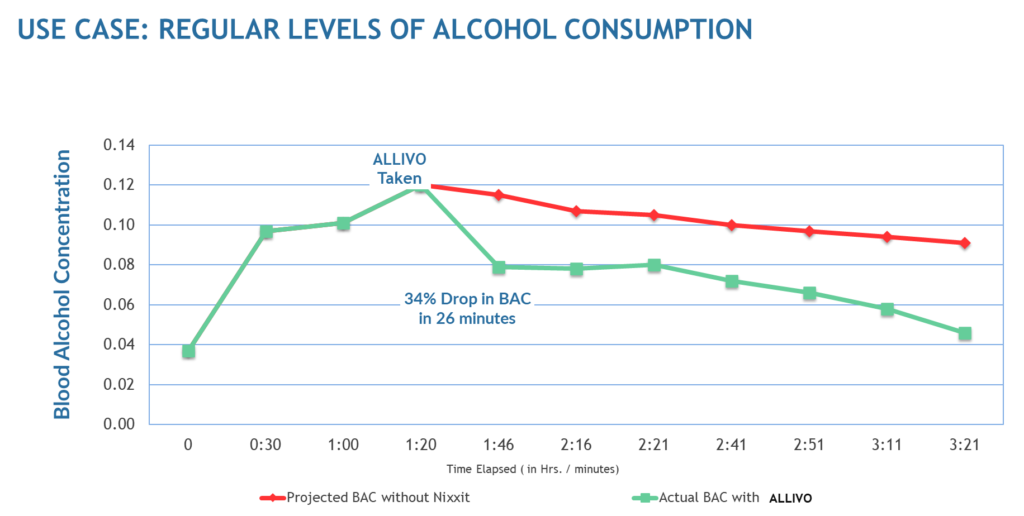
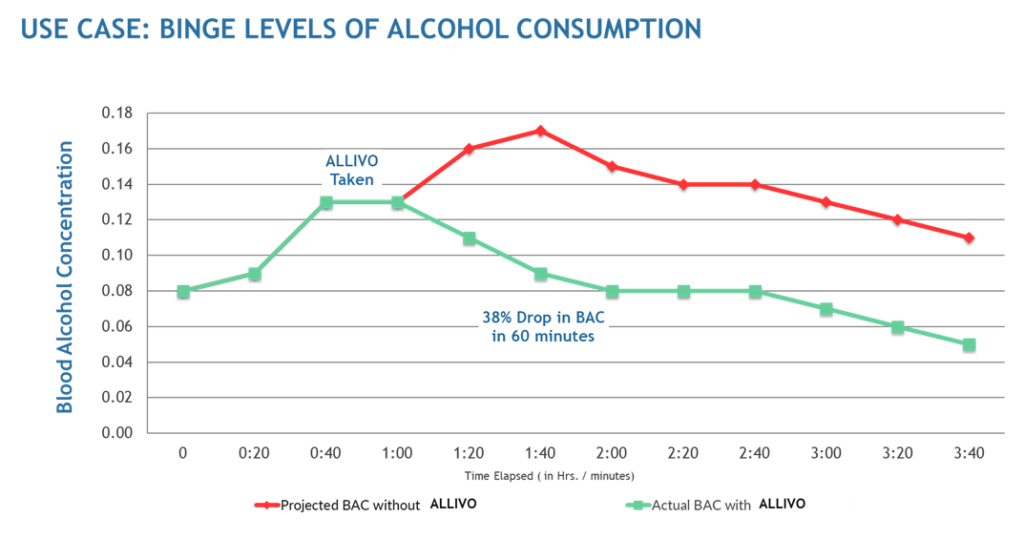
Note:Result vary based on the user’s physical characteristics (i.e. weight, body mass, sex, age, prior food and alcohol quantities consumed, etc.).
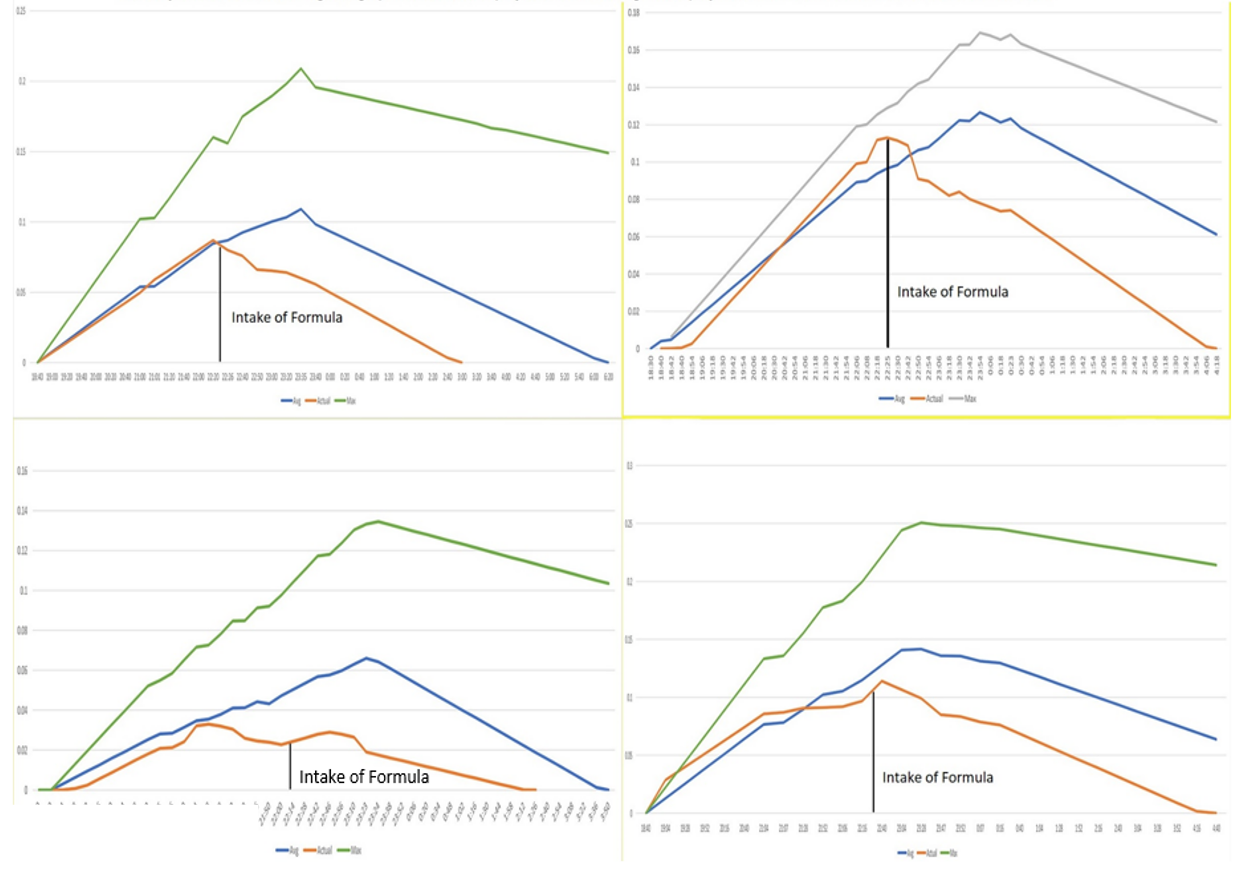
VOLUNTEER Trial RESULTS
A variety of volunteers participated in multiple tests. The 4 graphs below represent the response ranges of different biological profiles and alcohol consumption.
Initially, volunteers were asked to consume their drink of choice without taking the ALLIVO formula. Their blood alcohol concentration levels (BAC) were taken at the point they choose to stop drinking, then recorded at 15-minute intervals afterwards.
On a separate occasion, similar conditions were re-created (i.e. food and drink consumption), but this time volunteers took the ALLIVO formula when they stopped drinking. Their BAC levels were monitored in the same fashion for comparison. Both trial results are displayed in the charts below.
Every case participants experienced a rapid recovery of cognitive thought and motor functions

IMPORTANT NOTE:
These statements above have not been evaluated by the FDA. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent disease or alcoholism.
If you have any allergies, health or mitigating circumstances affected by probiotic consumption, you should first consult with your physician,
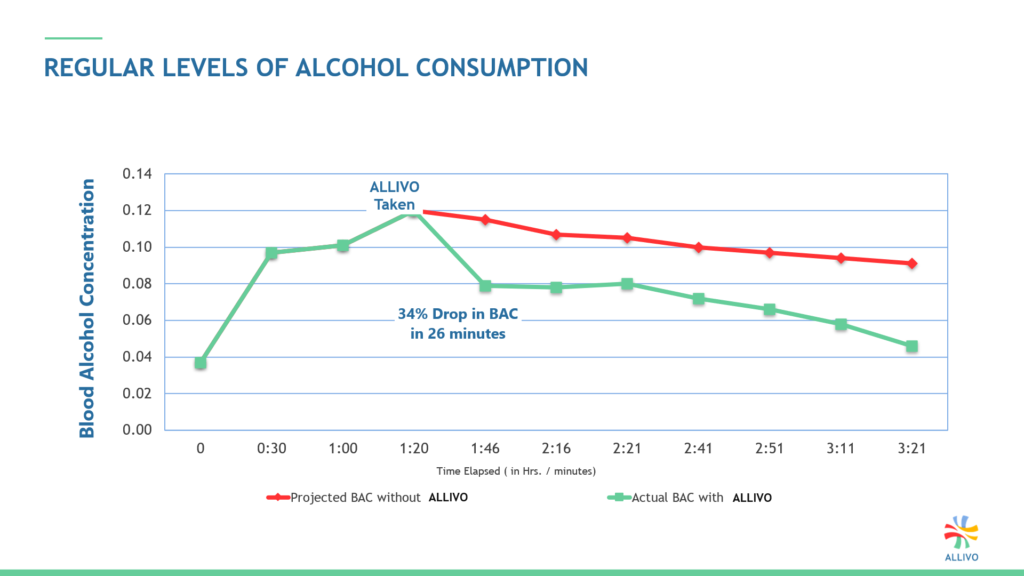
Regular levels of alcohol consumption
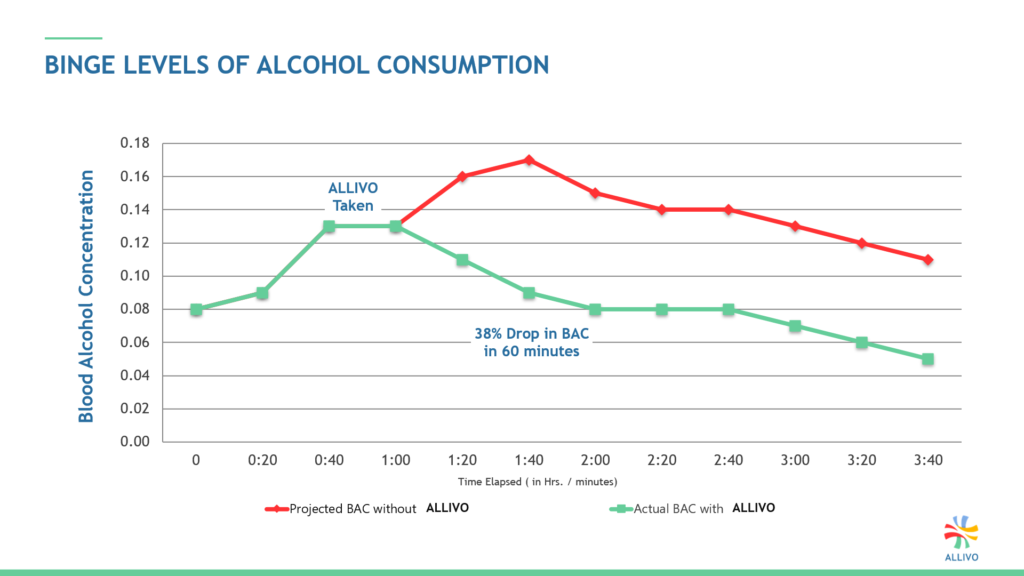
BINGE LEVELS OF ALCOHOL CONSUMPTION
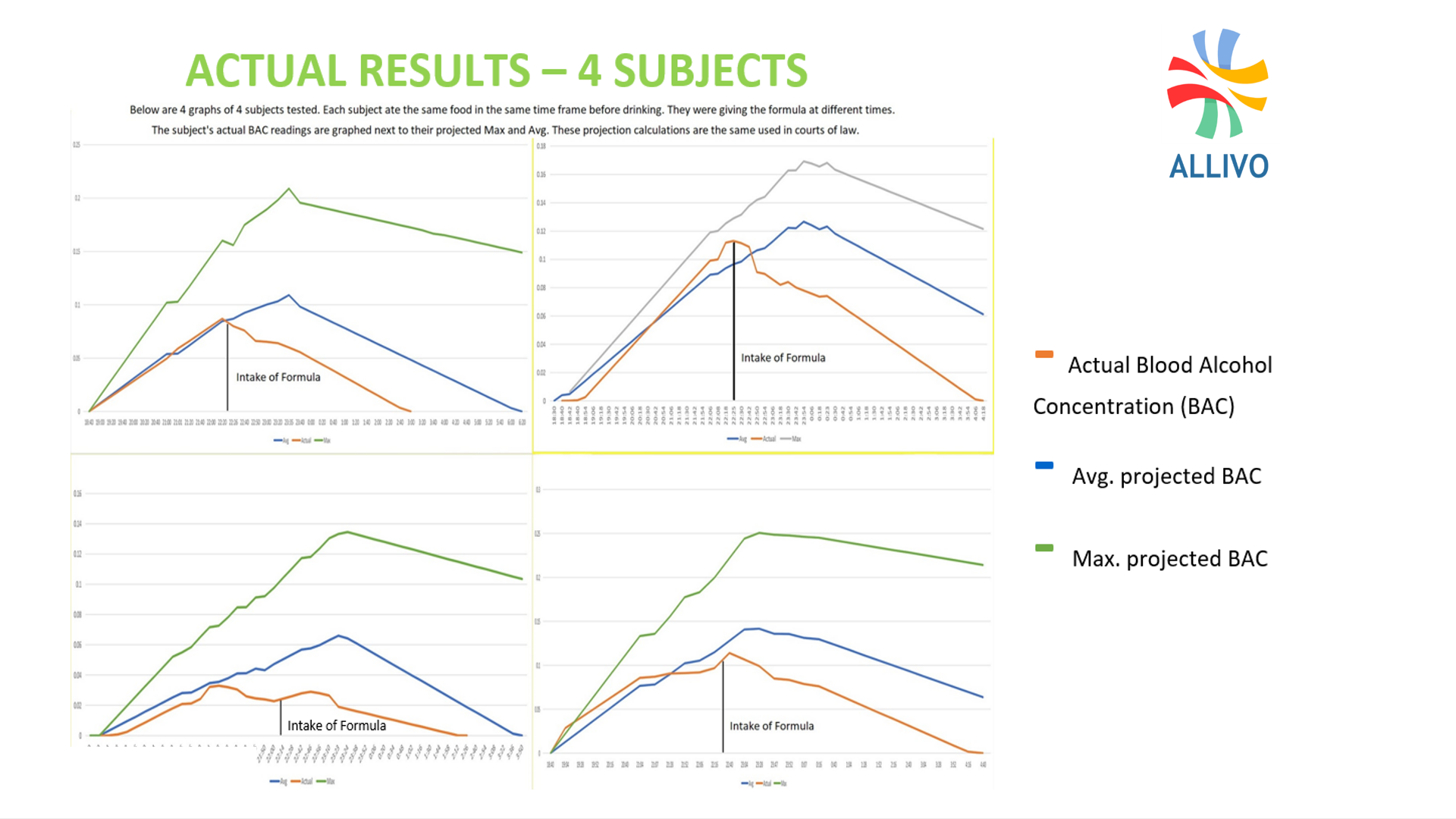
Actual results - 4 subjects
Below are 4 graphs of 4 subjects tested. Each subject ate the same food in the same time frame before drinking. They were giving the formula at different times. The subject’s actual BAC readings are graphed next to their projected Max and Avg. These projection calculation are the same used in courts of law.
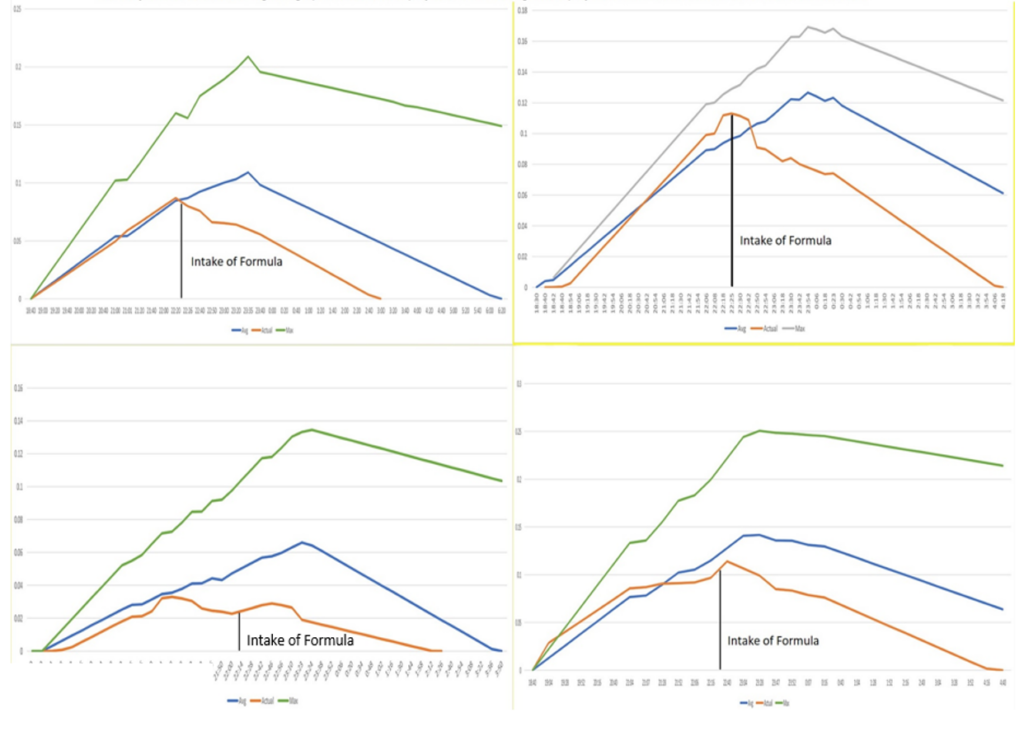

- Actual Blood Alcohol Concentration (BAC)
- Avg. Projected BAC
- Max. projected BAC
LOWER BLOOD ALCOHOL = FASTER RECOVERY

Science BEHIND ALLIVO'S CAPACITY


